Subtotal $0.00
Shopping cart
Subscribe to out newsletter today to receive latest news administrate cost effective for tactical data.
2478 Street City Ohio 90255
Contact Us
044-48595571
Monday - Friday
Subscribe to out newsletter today to receive latest news administrate cost effective for tactical data.
2478 Street City Ohio 90255
Contact Us
Monday - Friday

Individual approach

Safety and carefully

By professionals

Accurate approach
Preparing for Surgery

24x7
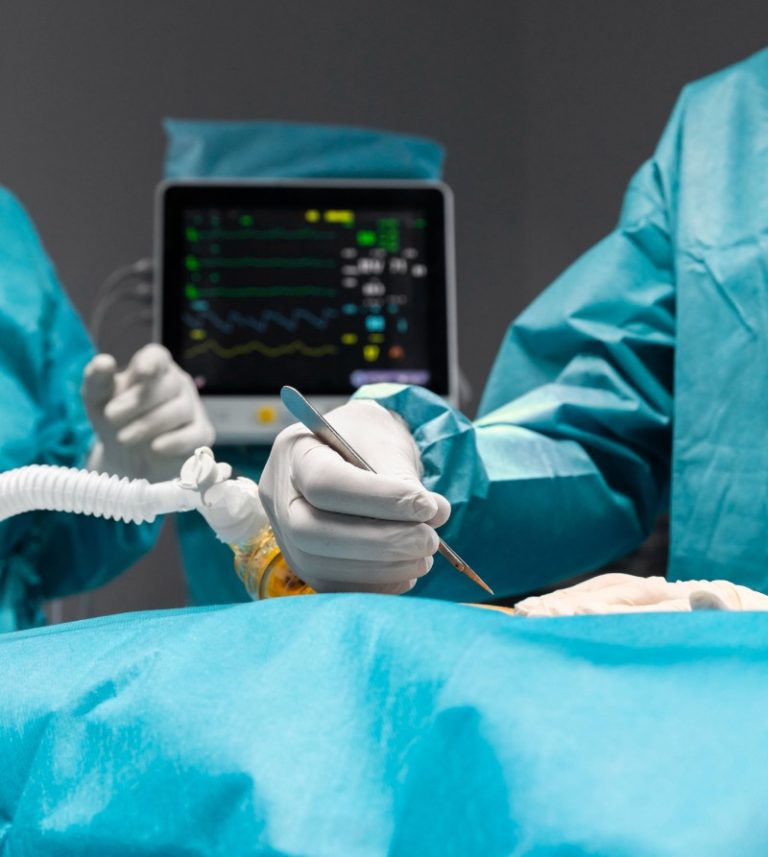
Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure orthopaedic surgeons use to visualize, diagnose, and treat problems inside a joint.
The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, “arthro” (joint) and “skopein” (to look). The term literally means “to look within the joint.”
Arthroscopic surgery
In an arthroscopic examination, an orthopaedic surgeon makes a small incision in the patient’s skin and then inserts pencil-sized instruments that contain a small lens and lighting system to magnify and illuminate the structures inside the joint. Light is transmitted through fiber optics to the end of the arthroscope that is inserted into the joint.
By attaching the arthroscope to a miniature television camera, the surgeon is able to see the interior of the joint through this very small incision rather than a large incision needed for surgery.
The television camera attached to the arthroscope displays the image of the joint on a television screen, allowing the surgeon to look, for example, throughout the knee. This lets the surgeon see the cartilage, ligaments, and under the kneecap. The surgeon can determine the amount or type of injury and then repair or correct the problem, if it is necessary.
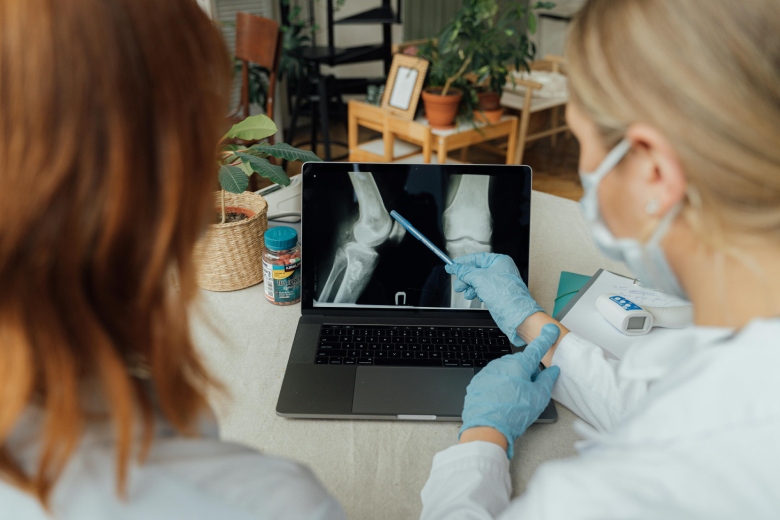

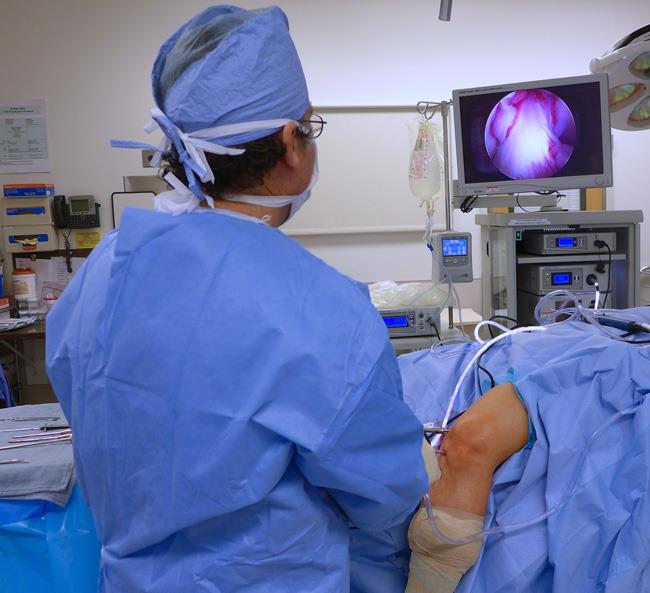
Diagnosing joint injuries and disease begins with a thorough medical history, physical examination, and usually X-rays. Additional tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) also scan may be needed. Knee Arthroscopy Exercise Guide Through the arthroscope, a final diagnosis is made, which may be more accurate than through “open” surgery or from X-ray studies. Disease and injuries can damage bones, cartilage, ligaments, muscles, and tendons. Some of the most frequent conditions found during arthroscopic examinations of joints are: Inflammation For example, synovitis is an inflammation of the lining in the knee, shoulder, elbow, wrist, or ankle.
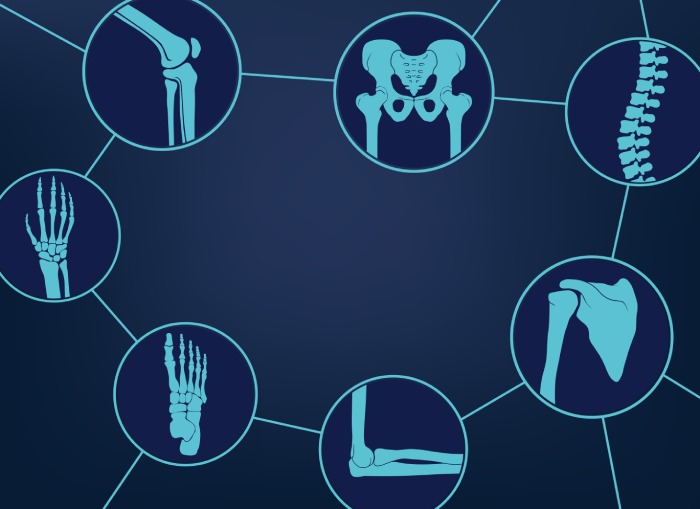
Rotator cuff tendon tears, impingement syndrome, and recurrent dislocations
Meniscal (cartilage) tears, chondromalacia (wearing or injury of cartilage cushion), and anterior cruciate ligament tears with instability
Carpal tunnel syndrome or example, knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle, or wrist
Some problems associated with arthritis also can be treated. Several procedures may combine arthroscopic and standard surgery.
Although the inside of nearly all joints can be viewed with an arthroscope, six joints are most frequently examined with this instrument. These include the knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle, hip, and wrist. As advances are made in fiberoptic technology and new techniques are developed by orthopaedic surgeons, other joints may be treated more frequently in the future.

Your care and comfort are our top priorities. We ensure that the patients are well informed prior to every step we take for their benefit and their queries are effectively answered.
The Sangam Bone and Joint Hospitals’ team stays up to date on the advancements in medical procedures and technologies. Experience the Future Healthcare Technologies now at Sangam Bone and Joint Hospitals.

Strengthening lives through compassionate care, innovative therapies and relentless efforts. It relentless efforts. It reflects in the DNA of our passionate team of doctors and dedicated clinical staff.